


Understanding Company Assets On The Balance Sheet.The Balance Sheet And Income Statement For Beginners.Financial Statements Glossary: Understanding Key Terms.Sustainability Accounting & ESG Simply Explained.
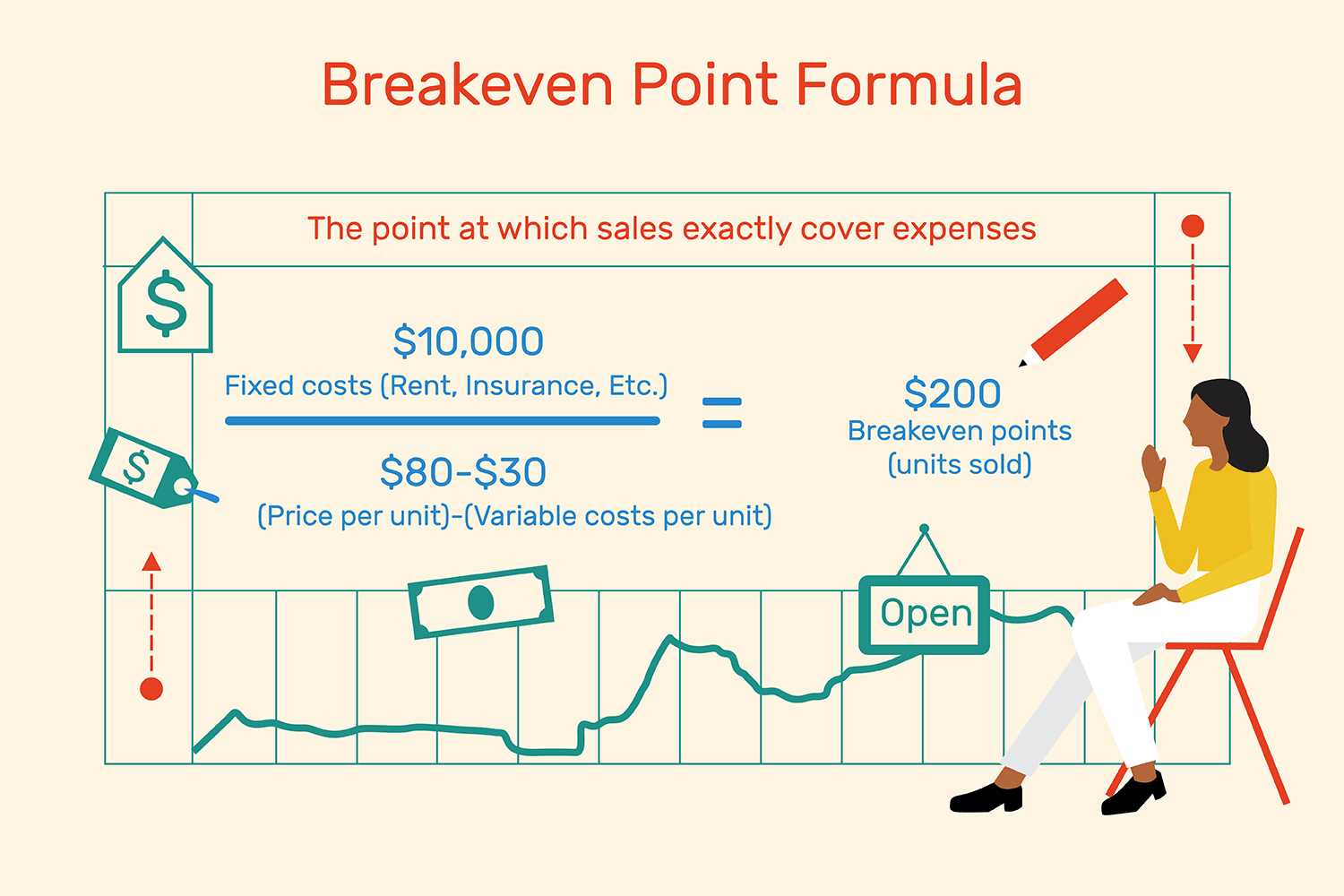
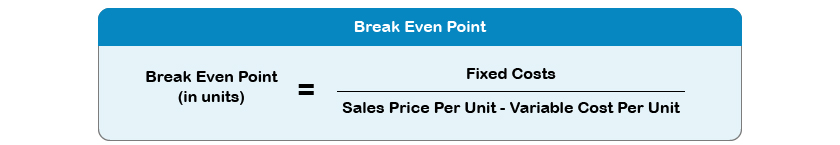
Pay As You Earn: An Overview With Examples.The Art of Crafting Effective Sales Invoices: Tips for Accountants.What Are Accounting Conventions, And Why Do They Matter?.What Are Accounting Ethics, And Why Do They Matter In Auditing?.The 5 Most Common Auditing Techniques In 2023 Simply Explained.Simplifying Sales Invoices: A Guide for Business Owners and Accountants.An Overview of Zakat and Zakat Declaration.8 Crucial Accounting Cycle Steps With Examples.International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Simply Explained.25 Essential Accounting Terms Everyone Should Know.When To Choose Accrual Accounting Over Cash Accounting.9 Fundamental Accounting Principles for Small Businesses.EBITDA: Calculation, Meaning, And Traits.Financial Forecasting In Accounting Explained.Projection Simply Explained With Examples The Accounting Equation Simply Explained.Project Management Skills For Accounting: An Overview.Accounting Career: What Can You Reach In The Field?.Understanding Government Accounting: A Comprehensive Overview.International Accounting Standards (IAS) Simply Explained.Financial Accounting: A Comprehensive Overview.Accounting Period Simply Explained With Examples.Recording Transactions In Accounting, Simply Explained With Examples.Bookkeeping And Accounting: The Differences You Should Know.Overview of Accounting in the Modern World.In this case, the business would need to sell 101 T-shirts to break even. In such cases, the business would always need to sell an additional item in order to break even. Sometimes the result is a little more complex, as the BEP may not be a whole number (eg 100.12). So this business breaks even when it sells 100 T-shirts. ExampleĪ business that sells T-shirts wants to find out what its BEP is. The calculation in brackets, which gives the contribution per unit, must be completed first. The result of this calculation is always how many products a business needs to sell in order to break even. You may also see this calculation written as:īreak-even output = Fixed costs ÷ (Selling price per unit− Variable costs per unit) Once the contribution per unit is found, the break-even output can be calculated:īreak-even output = Fixed costs ÷ Contribution per unit Firstly, a business must work out the contribution, this is calculated as:Ĭontribution per unit = Selling price per unit – Variable costs per unit This involves working out the contribution that each product sold provides towards the fixed costs of a business. Using break-even allows a business to understand its costs, revenue and potential profit to help inform business decisions.īreak-even can be calculated using the contribution method. The break-even level of output informs a business of how many products it needs to sell to reach the break-even point (BEP). Break-even is the point at which revenue and total costs are the same, meaning the business is making neither a profit nor a loss.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
